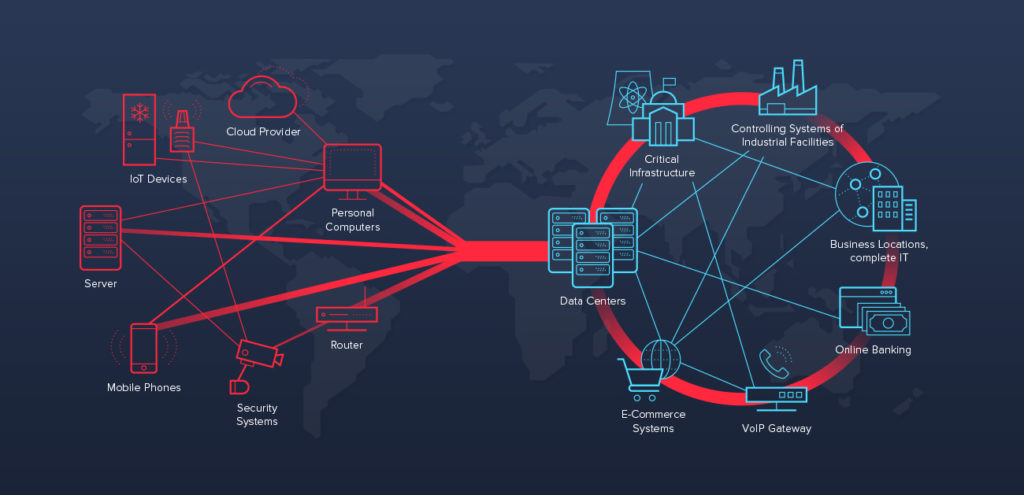
A Distributed Denial of Service attack, better known as a DDoS attack, is when a massive flood of intentional traffic congests a website, application, or network. Due to the fact that this service is often coming from an entire network of devices, it’s particularly difficult to locate where the attack is coming from.
A DDoS attack shouldn’t be confused with a DOS attack, with the main difference between these two being their scale. While a DDoS attack uses many devices to launch traffic, a DOS (Denial of Service) attack only uses one source. Considering the single location, it’s considerably easier to locate and stop a DOS attack rather than a DDoS attack.
With experts predicting that there will be over 15.4 million DDoS attacks over the next few years, there’s never been a better time to learn about these cyber threats.
Why Do DDoS Attacks Occur?
DDoS attacks are malicious attempts at preventing users from reaching the target site. This could be to stop a particular business from making sales, or to simply prevent users from accessing a website.
A typical DDoS attack will either slow down or altogether disable a website for a period of time, resulting in substantial financial losses if enacted on a site that requires customers to pass through their store. If launched on an eCommerce store, this is a particularly malicious attack, effectively disabling the business’ ability to generate a profit.
Even when only slowed down, rather than entirely disabled, the extra bounce rate of the site causes many customers to click off the site and come back later. Considering that the average US consumer will only wait 3.4 – 3.9 seconds before clicking off a page, even slowing down a site can have disastrous consequences.
How Do DDoS Attacks Work?
A DDoS attack functions by sending a spike of traffic directly to a website, overloading its capacity and meaning that the server cannot respond efficiently. These fake traffic spikes are mostly generated by one hacker using a Botnet.
A Botnet is a network of compromised devices, be it mobile phones, computers, or laptops, that the hacker can control remotely and command to go to a specific site. With 100s or even 1000s of devices controlled within a single Botnet, a hacker can send an enormous amount of traffic to one network site with the click of a button.
Once an attacker has tested the limit of a network server they want to attack, they’ll then work out how much traffic they need to send over to that site to disable it. The more traffic that attempts to enter that site simultaneously will result in the website slowing down to accommodate for the spike.
As the server reaches total capacity and then goes beyond its limits, the website will completely shut down due to the extreme demand placed upon it by the hacker’s Botnet.
What Are the Signs of A DDoS Attack?
While there are several common DDoS attack types, they all have similar effects on the website. The main difference between the various DDoS attacks is the method they use to reach the website and the scale of the attack. Even with the smallest or least severe form of DDoS attacking, you’ll likely see the following signs:
- Running Slowly
- Unresponsive Pages
- Slow computer performance
Let’s break these down further.
Running Slowly
As the traffic to your site increases, the strain on your hosting server will also increase. Due to this, the ping rate between your site and the server will begin to take longer and longer, meaning your site will run slower.
What once may have taken under a second to load may now take minutes at a time, the information being contested on its path.
Unresponsive Pages
As your site reaches its server capacity, pages will start to go offline. Starting with periphery or less visited pages, your site will begin to shut down and become completely unresponsive.
Eventually, this will extend to the homepage, with users being unable to access your site at all.
Slow Computer Performance
Suppose you, yourself, are the victim of a DDoS attack. In that case, your computer will likely slow down as its network becomes unresponsive and congested.
A DDoS attack on a personal network can lead to issues with connecting to the internet, staying online, and navigating through your computer’s pages.
What are the effects of a DDoS attack?
Alongside slowing down your site’s server, a DDoS attack can have long term impacts on your website. The three most common effects of DDoS attack are:
- Site Vulnerability – As all of your site’s security services will be focusing on getting your site back up and running, your website is much more vulnerable to backdoor entry and more general hacking.
- Financial Loss – Any moment that your business is offline is a moment in which you’re making potential financial losses. The more time your site is down for, the more money your business loses.
- SERP Ranking Impact – If search engines routinely index your site and notice that it is producing a 502 bad gateway error, they will start to rank you lower on their rankings systems, further impacting the success and longevity of your business.
Final Thoughts on DDoS Attacks
Considering that over the first 6-months of 2020, the internet saw a 151% increase in these attacks, cybersecurity breaches are becoming more common than ever before. No matter if you’ve never experienced an attack or are routinely suffering from them, it’s a great idea to know the signs.
Be sure to understand both the signs and effects of DDoS attacks so that you’ll be better prepared to deal with them. You’ll also be able to prepare your website to defend against these types of attacks as a precaution.
Have you ever experienced a DDoS attack? Let us know down in the comments below!