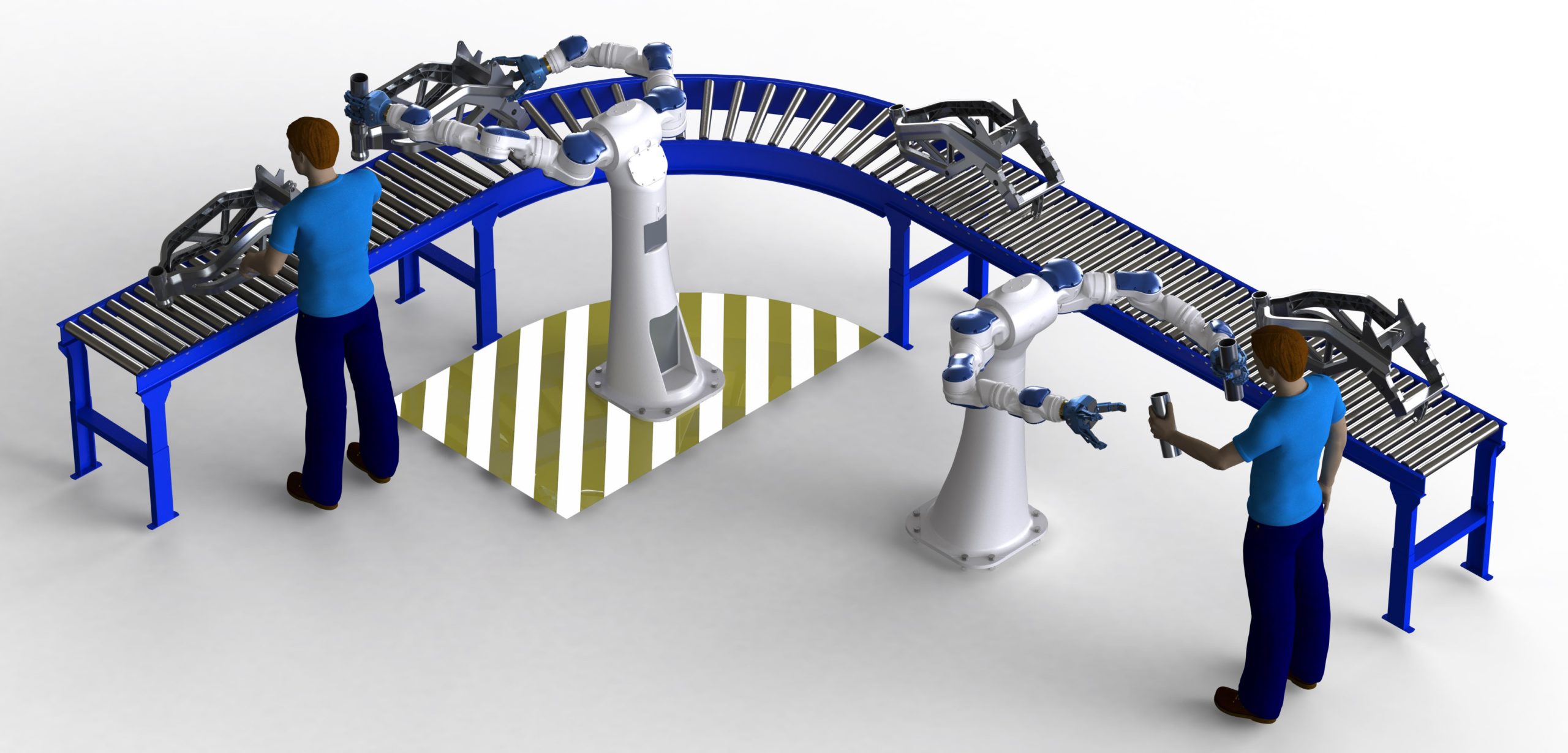
Robotics in the 21st century has greatly advanced, and where robotics sounded like a Sci-Fi dream, it is now a reality. Robots are widely in use, especially in the manufacturing industry. There are various types of robots in use in the automotive industry.
Automotive robots are machines that are computer programmed to automatically perform various actions. There are various robotic applications for automotive robots, and they can be autonomous or semiautonomous.
Robotic Applications in the Automotive Industry
Automotive industries took a long time to adapt to robotics, but are now among the quickest to adopt any new technology. Various robotic applications are in use in the automotive industry such as:
- Collaborative robots
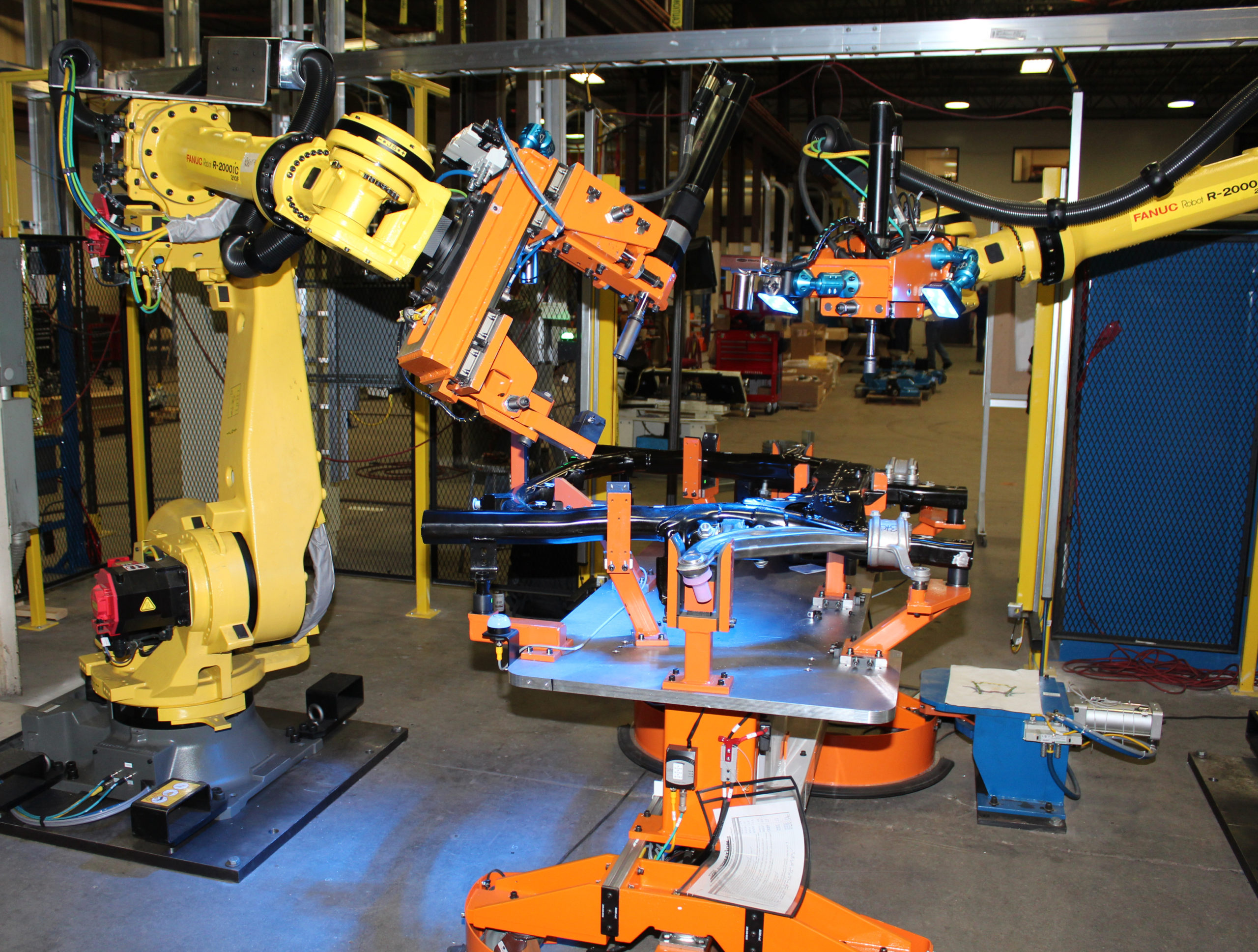
Collaborative robots comprise inbuilt robots that work alongside other robots. These robots are mostly used in automobile assembly plants. Welding and assembly automotive robots ensure that everything in the assembly lines runs smoothly.
- Robotic Painting
Automotive painting is toxic for humans, and robots are used to paint vehicles and reduce risk to humans. Robots are perfect for pulling off the painting of large areas and are more consistent than humans can be. The automotive robots also work faster than humans, thus increasing the output.
- Robotic Welding
A vehicle needs a lot of welding before it is termed as complete. This welding is done under extremely high temperatures that may pose a health risk to humans. Robotic welding has become an invaluable part of the automotive industry as robots do a perfect job with fewer errors.
- Robotic Assembly
The assembling of tiny components such as motors or pumps is effectively done by automotive robots. The robots are also useful in installing windshields and mounting wheels with precision and speed.
- Material Removal
Automotive robots are useful in automotive industries for cutting and trimming for material removal. The robots are very precise and do perfect fabric cutting and plastic trimming.
- Part Transfer and Machine Tending
The automotive industry involves a lot of heavy material transfer and pouring of hot molten metal, which is dangerous to humans. In these cases, automotive robots are best suited for such jobs
Types of Automotive Robots
There are several types of automotive industrial robots, with the most common being:
- Cartesian Robots
These are three-jointed robots. The robots are named so because they use the Cartesian coordinates of X, Y, and Z.
- Articulated Robots
Articulated robots are built of rotary joints, which consist of two bolts to at least ten or more joints. The robot’s arm is connected to a bottom or base with a joint that twists to and from for movement enhancement. Most automotive joints have between four and six joints.
- Cylindrical Robots
Cylindrical robots are made of a single rotary joint at its base and another that joins the links. This robot works in a cylindrical object.
The type of robot used depends on what it is used for, and the company’s space. Some robots have a small footprint and can work in tiny spaces, while others require large spaces because of their large footprint.
Robotic Nature
The automotive robots’ nature can either be autonomous or semiautonomous.
- Autonomous Robots
Autonomous robots do not take directions from users. The robots are intelligent and perform their programmed tasks without human intervention. The robots are known for their precision and near-perfect jobs.
The autonomous robots’ advantage is that once they are programmed, no human input is necessary as they work autonomously or independently.
- Semi-Autonomous Robots
Semi-autonomous robots perform their tasks and make decisions without needing direction. However, they take commands from the users, and a controlling device can be used to guide the robots. Semi-autonomous robots are useful in the manufacturing industry since the external controlling device can be used to start or stop a process when necessary. The type of robot used is dependent on the tasks’ nature and the robots can be used to perform different functions with the needed precision.
Conclusion
The automotive industry has come a long way, and the use of automotive robots helps in minimizing health risks and injuries to human workers and improving the quality of the vehicles.