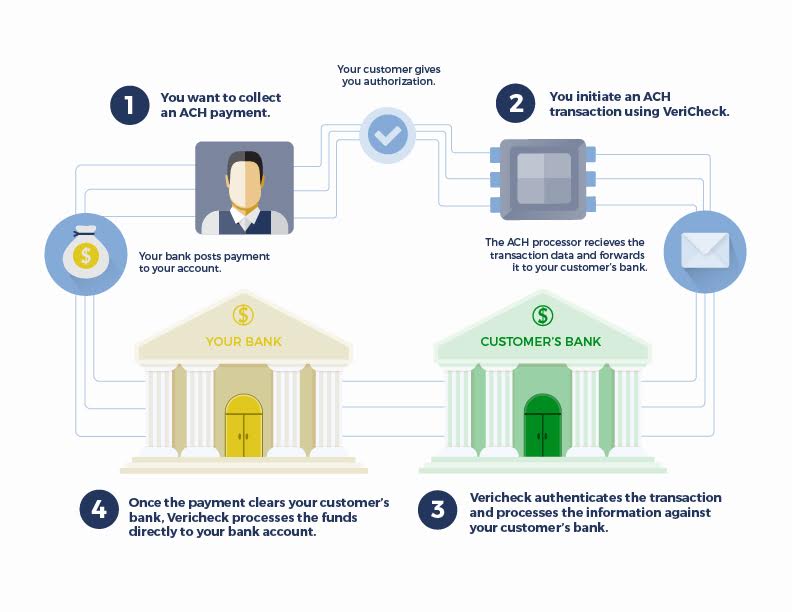
ACH payment processing is used by enterprises of all size. The ACH acronym stands for Automated Clearing House. It is a highly vetted electronic network that makes it possible for people to transfer funds directly between two bank accounts. Billions of dollars are processed through ACH payments in the United States annually. Many of the transactions are direct deposits from employers to employees. However, this method can be used for a wide variety of payment types. There are several benefits for enterprises to use ACH payments. Here are a few of the top perks:
● Low transaction fees
● Convenience
● Reduction in human error
● Quick processing times
Due to these benefits, ACH payment processing has become a mainstream option. However, the popularity and convenience of ACH payment processing does not make it immune to the risk of fraud. In fact, ACH payments are increasingly being targeted by hackers and thieves.
Staying Protected When Using ACH Payment Processing
It is extremely important for enterprises to have a system in place for spotting any inconsistent activities or anomalies that pop up in the payroll process or accounts payable process if they are using ACH payment processing. Enterprises must have safeguards in place to limit exposure when it comes to new billing parties. More and more enterprises are turning to big data platforms to increase financial fraud prevention and detection. Having an internal system in place for spotting fraud can close vulnerabilities that make an enterprise an easy target for both internal and external fraud.
The Fraud Risks Within ACH Payment Processing
While popular, ACH payment processing is vulnerable to several types of fraud. The most prevalent type of fraud that affects ACH payment processing is payroll fraud. Payroll fraud occurs in 27 percent of all businesses. Payroll fraud is twice as likely to occur in small organizations with fewer than 100 employees. Automation of the payment process makes it easy for employees to commit fraud by fabricating hours, failing to pay back advances or creating ghost accounts for nonexistent employees. Hackers from outside of an enterprise can also perpetrate fraud by taking advantage of blind spots in the ACH payment processing system. Criminals can find ways to break into banking accounts and pretend to be customers. Phishing schemes or social engineering can be used to gain access to a person’s computer or an enterprises’ network. Funds can be diverted to fraudulent accounts once a hacker is able to make changes to a payroll account.
ACH kiting is another form of fraud that can potentially affect enterprises using ACH payment processing. A bogus company posing as a charity or client can send out a bill for a large sum of money to the enterprise it is targeting. That bogus company will then appear to have a large amount of credit sitting in its bank account. The victim is often unaware of what is going on because the charge is sitting unnoticed in an account. The bogus company will then get ahold of the money and disappear by the time the charge is noticed and contested. Banks are often unable to spot this form of fraud due to the high volume of payments coming in and being credited back at any given time.
Safeguarding your accounts from unauthorized ACH debits and credits plays a crucial role in preventing debilitating fraud. Big data can help transform the known data surrounding ACH payment processes in actionable insights.