Kubernetes is an open-source platform for managing containerized workloads and services. Kubernetes clusters are collections of components that form nodes. These nodes run containerized application packages that are more lightweight and flexible than virtual machines.
Using a Kubernetes cluster makes developing and managing an application easier. Let’s learn more about Kubernetes clusters.
What Are Kubernetes Clusters?
If you use a Managed Kubernetes service, you’re running a Kubernetes cluster. This system offers many advantages, including scheduling and running containers across a group of machines. Kubernetes containers are not tied to individual machines. Instead, they are distributed across a cluster.
Kubernetes clusters have one master node and several worker nodes. Depending on the cluster, these may be physical computers or virtual machines. Kubernetes clusters can run containers under any operating system. They also run across multiple machines or environments, whether physical or virtual, cloud-based or on-premises.
Master Nodes and Worker Nodes
For a Kubernetes cluster to be operational, you must have at least one master node and one worker node.
The master node controls the cluster state, deciding which applications are running and their corresponding container images. It coordinates application scheduling and scaling, maintains cluster state, and implements updates.
The worker nodes receive instructions from the master node and run the applications accordingly. A worker node performs the tasks, operating as part of a single system.
They host pods, which are components of the application workload. The control plane manages the cluster worker nodes and pods. It typically runs multiple nodes at once to guard against failure, ensuring high availability.
Components of a Kubernetes Cluster
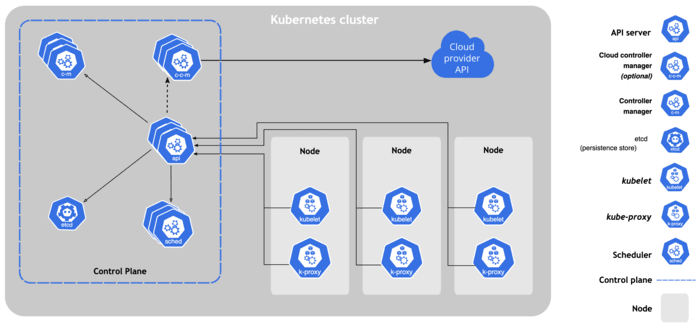
Inside a Kubernetes cluster, you have six primary components, each running on either the master node or worker nodes. These form the control plane and allow the user to decide how to use their Kubernetes cluster. They also detect and respond to events.
Component #1: API Server
The API server is the front end of the Kubernetes control plane, providing the interface to all Kubernetes resources. It scales horizontally. Several instances of the API server can be run simultaneously with traffic balanced between them.
Component #2: Scheduler
The scheduler analyzes resource requirements and metrics to place containers appropriately. Schedulers consider hardware or software constraints, affinity and anti-affinity specifications, data locality, inter-workload interference, and deadlines. If pods have no assigned nodes, such as newly created pods, the scheduler selects nodes for them to run on.
Component #3: Controller Manager
The controller manager, like the API server and scheduler, runs on the master node. A controller manager runs controller processes and reconciles a cluster’s actual state under specific conditions.
In this, you have a tool that manages node, endpoint, and replication controllers. Each controller is separate but compiled in a single binary and executed in a single process.
Component #4: Kubelets
Kubulets ensure containers run in a pod. It runs on each node in a cluster. Kubelets do not manage containers Kubernetes did not create. A kubelet will interact with the docker engine, a default program for creating and managing containers.
Component #5: Kube-Proxy
The kube-proxy oversees network connectivity and enforces network rules across nodes. It implements the Kubernetes Service concept across all nodes in the cluster. These network rules allow communication between your pods from network sessions inside or outside your cluster.
Component #6: Etcd
Etcd stores all cluster data in a consistent, highly available key-value store. When using etcd as your backing store for a Kubernetes cluster, a backup plan for the data is best established to define how that occurs.
Running Kubernetes Components
Kubernetes components can be run on any machine in the cluster. Typically, they are deployed on a dedicated machine for isolation and simplicity. Most setup scripts start control plane components on the same machine. They usually do not run user containers on this machine.
The control plane runs continuous control loops to ensure a Kubernetes cluster’s actual state matches its desired state. If a replica crashes, for example, the Kubernetes control plane registers it and deploys an additional replica to maintain the desired state.
Define the desired state of the Kubernetes cluster before using it. You can do so through JSON or YAML files. The desired state of a Kubernetes cluster defines how it works. It will decide what applications and workloads to run. Also, it determines the images that need to be used, the resources provided, and the number of replicas required.
Multiple Kubernetes Clusters
You can manage multiple Kubernetes clusters effectively for complex projects and across various teams. Namespaces are a vital tool within a single physical cluster, allowing users to organize and separate resources for different teams or projects. You can implement resource quotas within namespaces to manage resource consumption.
You can create and deploy a Kubernetes cluster on a physical or virtual machine. For beginners, users may appreciate Minikube’s easy functionality, an open-source tool compatible with Linux, Mac, and Windows operating systems.
Minikube is an excellent starting point for learning how a Kubernetes cluster works. It allows users to create and deploy a cluster containing only one worker node.