As cyber threats continue to evolve and traditional security perimeters dissolve, organizations are increasingly adopting Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) as their primary cybersecurity framework.
This paradigm shift from implicit trust to continuous verification represents one of the most significant changes in enterprise security strategy in recent years.
Understanding how to implement Zero Trust effectively has become crucial for modern businesses seeking to protect their digital assets.
Understanding Zero Trust Fundamentals
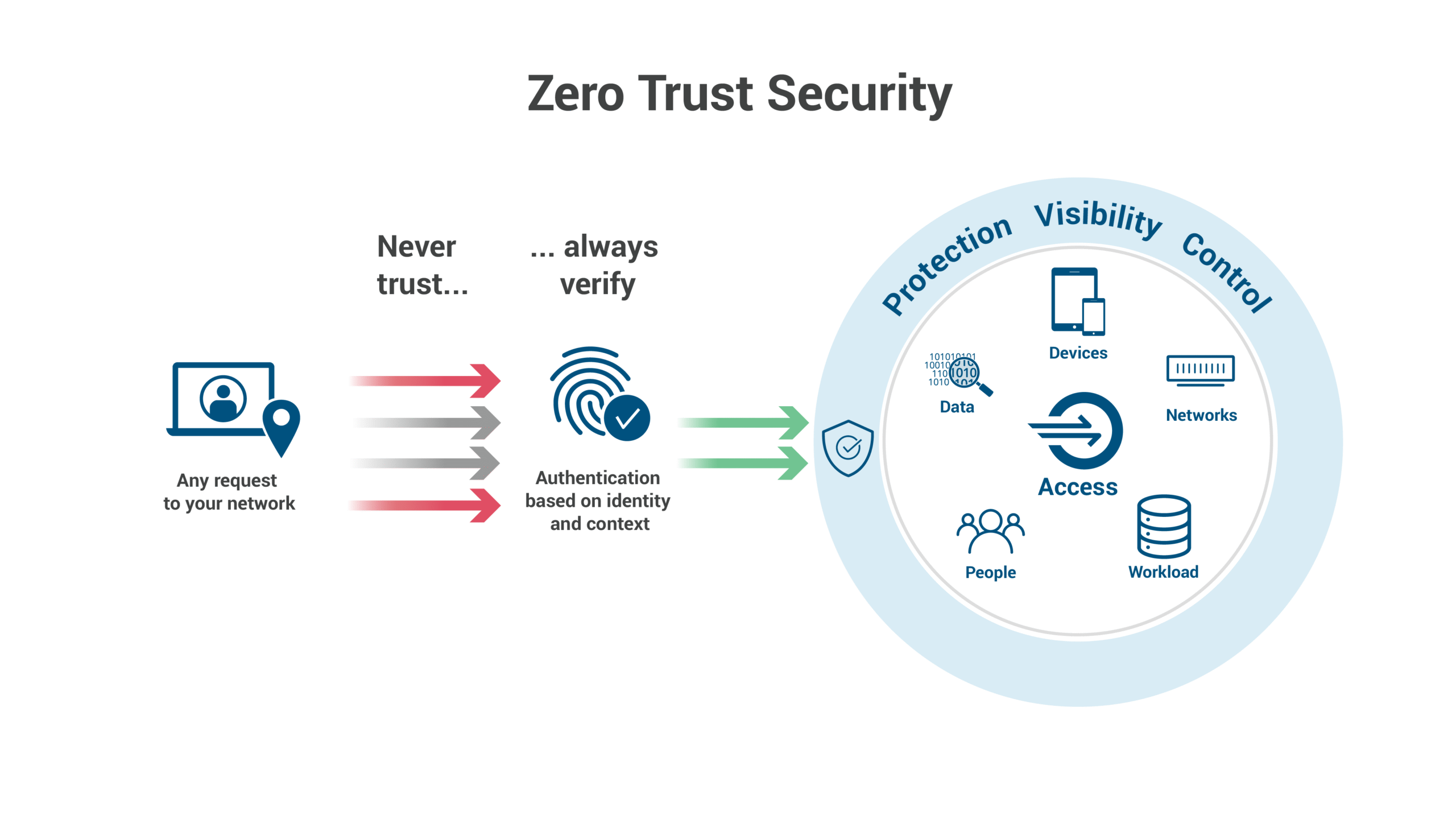
Zero Trust operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” fundamentally challenging the traditional castle-and-moat security model.
Unlike conventional approaches that assume everything inside the network is trustworthy, Zero Trust treats every user, device, and application as potentially compromised until proven otherwise through continuous authentication and authorization processes.
The architecture rests on three core principles: explicit verification of every transaction, least-privilege access controls, and assumption of breach scenarios.
These principles work together to create a comprehensive security framework that adapts to modern distributed computing environments where data, applications, and users exist across multiple locations and platforms.
Strategic Implementation Framework
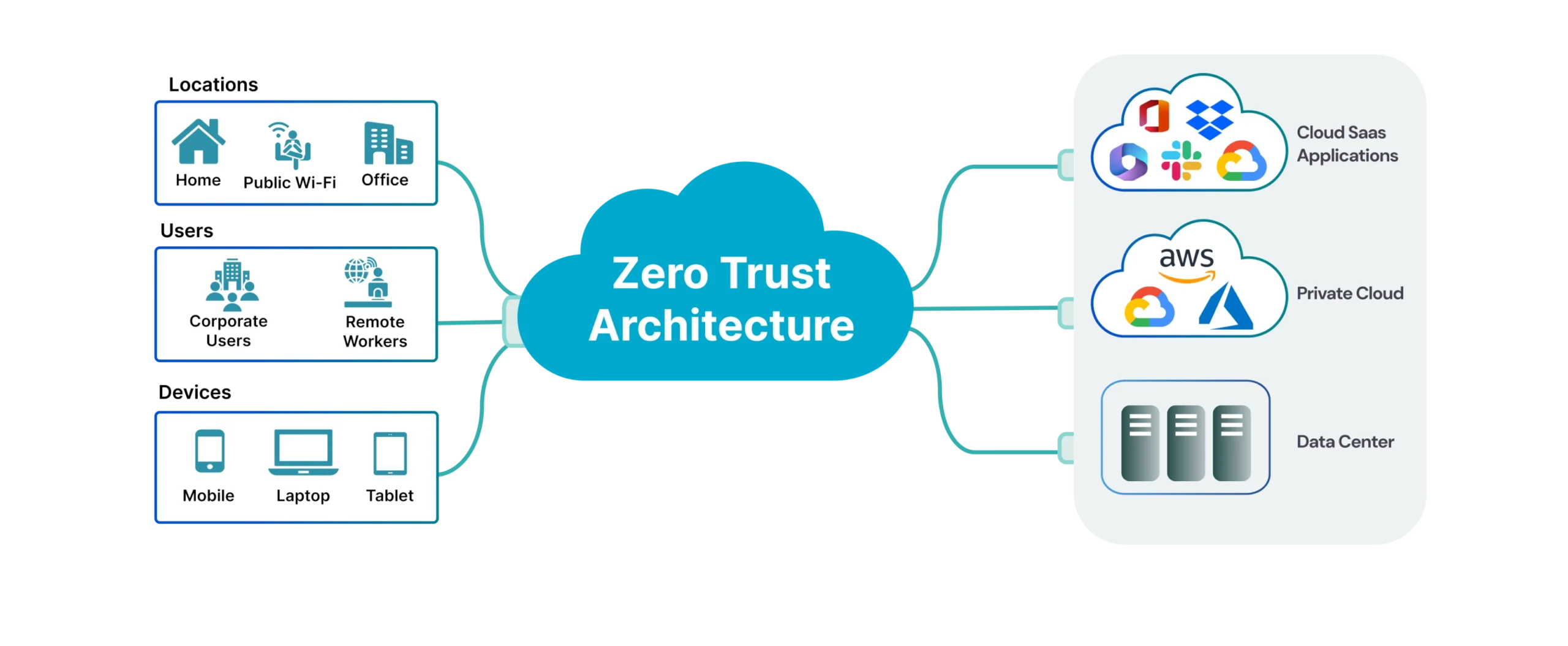
Successful Zero Trust implementation requires a structured approach that begins with comprehensive asset discovery and risk assessment.
Organizations must first map their entire digital ecosystem, identifying all users, devices, applications, and data flows. This visibility forms the foundation upon which Zero Trust policies are built and enforced.
The implementation typically follows a phased approach, starting with the most critical assets and gradually expanding coverage across the entire infrastructure.
Beginning with high-value data and applications allows organizations to demonstrate immediate security improvements while building momentum for broader adoption throughout the enterprise.
Identity and access management (IAM) serves as the cornerstone of Zero Trust implementation. Modern IAM solutions must support multi-factor authentication, single sign-on capabilities, and dynamic risk assessment based on user behavior, location, and device characteristics.
These systems continuously evaluate access requests against established policies, granting the minimum necessary permissions for users to complete their tasks.
Network Segmentation and Microsegmentation
Network segmentation plays a crucial role in Zero Trust architecture by creating smaller, isolated security zones that limit the potential spread of security breaches.
Microsegmentation takes this concept further by creating granular security perimeters around individual applications, services, or even specific data sets.
Software-defined perimeters (SDP) and secure access service edge (SASE) technologies enable organizations to implement dynamic segmentation that adapts to changing business requirements and threat landscapes.
These technologies create encrypted tunnels between users and resources, ensuring that network traffic remains protected regardless of the underlying infrastructure.
Device and Endpoint Security Integration
Zero Trust extends security controls to all devices accessing organizational resources, whether corporate-owned or personal devices used in bring-your-own-device (BYOD) scenarios.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions provide continuous monitoring and threat detection capabilities, while mobile device management (MDM) platforms ensure that devices meet security standards before accessing sensitive resources.
Device trust evaluation considers factors such as operating system versions, installed applications, security patch levels, and behavioral anomalies.
This continuous assessment enables organizations to make real-time access decisions based on device risk profiles and compliance status.
Industry Applications and Security Innovation
The principles of Zero Trust Architecture have found particular relevance in industries handling sensitive data and financial transactions.
The online gaming and digital entertainment sector exemplifies how modern security frameworks must adapt to protect both user data and financial transactions in real-time environments.
Online casinos and gaming platforms have become pioneers in implementing advanced security measures that align with Zero Trust principles. These platforms must continuously verify user identities, monitor transaction patterns, and protect against sophisticated fraud attempts while maintaining seamless user experiences.
The latest technology being used in casino games demonstrates how real-time risk assessment and behavioral analytics can be integrated into user-facing applications without compromising performance or user satisfaction.
This convergence of security and user experience in the gaming industry provides valuable insights for other sectors seeking to implement Zero Trust while maintaining business agility and customer satisfaction.
Data Protection and Encryption Strategies
Data-centric security forms another pillar of Zero Trust implementation, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected regardless of where it resides or how it’s accessed.
Data classification schemes help organizations identify and apply appropriate protection measures based on information sensitivity and regulatory requirements.
Encryption strategies must address data at rest, in transit, and in use scenarios. Modern encryption technologies, including homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation, enable organizations to process sensitive data while maintaining privacy and security controls throughout the data lifecycle.
Monitoring and Analytics Integration
Continuous monitoring and analytics capabilities provide the intelligence necessary to support Zero Trust decision-making processes.
Security information and event management (SIEM) platforms, enhanced with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, analyze patterns across users, devices, applications, and network traffic to identify potential security incidents.
User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) solutions establish baseline behaviors for users and systems, enabling the detection of anomalous activities that may indicate security threats.
These analytics platforms integrate with automated response systems to enable rapid threat containment and remediation.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Organizations implementing Zero Trust often face challenges related to legacy system integration, user experience impacts, and operational complexity.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and phased implementation approaches that minimize disruption while building security capabilities incrementally.
Change management becomes critical as Zero Trust implementation often requires significant shifts in how users interact with systems and data. Training programs and communication strategies help ensure that security improvements don’t negatively impact productivity or user satisfaction.
Future Considerations and Evolution
Zero Trust Architecture continues to evolve as new technologies and threat vectors emerge. Cloud-native security tools, artificial intelligence integration, and quantum-resistant encryption technologies will shape the future of Zero Trust implementations.
Organizations must remain adaptable in their approach, regularly reassessing their Zero Trust strategies against emerging threats and changing business requirements.
The architecture’s inherent flexibility enables continuous improvement and adaptation to new security challenges while maintaining core security principles.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Architecture represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach cybersecurity, moving from perimeter-based defenses to comprehensive, continuous verification systems.
Successful implementation requires strategic planning, phased deployment, and ongoing commitment to security improvement.
As digital transformation accelerates and threat landscapes become increasingly complex, Zero Trust provides the framework necessary to protect modern enterprises while enabling business agility and innovation.
Organizations that invest in proper Zero Trust implementation today will be better positioned to handle tomorrow’s security challenges.