Resilience is a cornerstone of success in the intricate landscape of modern business. Companies face many challenges, ranging from regulatory compliance to operational risks. Organizations turn to frameworks that offer structured guidance to navigate these complexities effectively.
The COSO Framework emerges as a beacon, providing a comprehensive approach to bolstering resilience. This article delves into the COSO framework: a business compliance guide, the essence of the COSO Framework components, and how they contribute to building organizational resilience.
Understanding the COSO Framework
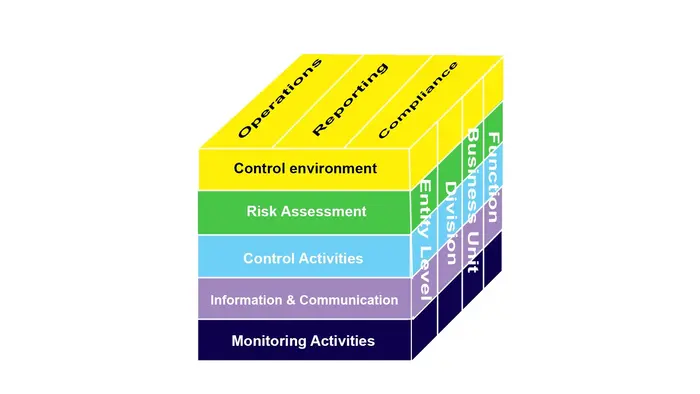
Before delving into its components, it’s crucial to grasp the essence of the COSO Framework. Established by COSO, this framework offers a structured approach to internal control, enterprise risk management, and fraud deterrence. At its core, it aims to enhance organizational performance and ensure sustainable growth.
Control Environment
The control environment serves as the bedrock upon which the edifice of effective internal control is erected. It is not merely a static entity but a dynamic force that reverberates through the organization. The tone set by management resonates deeply, shaping the ethos of integrity and ethical conduct that underpins every facet of operations.
Moreover, the competence level of personnel is not merely a matter of individual aptitude but a collective reflection of organizational capability.
By nurturing a culture of accountability and integrity, companies fortify their control environment, fostering an atmosphere where adherence to policies and procedures becomes second nature. This ethos permeates throughout all echelons of the organization, from the executive suite to the frontline staff.
It instills a shared sense of responsibility, where each member understands their role in safeguarding assets, ensuring compliance, and upholding the organization’s reputation.
A robust control environment is not just a regulatory requirement but a strategic imperative. It serves as a bulwark against internal and external risks, shielding the organization from potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Beyond mere compliance, it fosters trust among stakeholders, reassuring investors, customers, and regulators alike. In essence, the control environment is not just the foundation of effective internal control; it is the cornerstone of organizational resilience and longevity.
Risk Assessment
In the dynamic landscape of business, risk assessment is paramount. This component involves identifying, analyzing, and managing risks that could impede the achievement of organizational objectives.
Companies can proactively mitigate threats and capitalize on opportunities by conducting comprehensive risk assessments, fortifying their resilience against unforeseen challenges.
By systematically evaluating potential risks, organizations gain a deeper understanding of their operating environment, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Moreover, robust risk assessment processes facilitate the allocation of resources to areas of highest vulnerability, optimizing the organization’s risk-return profile.
Additionally, conducting regular risk assessments fosters a culture of risk awareness and accountability, empowering employees at all levels to determine and report potential risks promptly.
This proactive approach not only enhances the organization’s ability to anticipate and respond to emerging threats but also cultivates a competitive advantage in rapidly evolving markets. In essence, risk assessment serves as a cornerstone of effective risk management, enabling organizations to navigate uncertainties with agility and confidence.
Control Activities
Control activities constitute the policies, procedures, and mechanisms that ensure management directives are carried out effectively and efficiently.
These activities encompass various processes essential for the smooth functioning of the organization, including approvals, authorizations, verifications, reconciliations, and periodic reviews.
By embedding control activities within operational processes, companies establish a framework that promotes adherence to established protocols and standards. This enhances the reliability of financial reporting and safeguards assets against misappropriation or misuse.
Moreover, robust control activities serve as a deterrent against fraudulent activities, as they create checkpoints and validation procedures that detect anomalies and irregularities.
Furthermore, control activities facilitate compliance with regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies, thereby reducing the organization’s exposure to legal and reputational risks. Additionally, they promote operational efficiency by streamlining workflows and identifying areas for optimization.
Ultimately, the effective implementation of control activities fosters transparency, accountability, and trust within the organization, laying the groundwork for sustainable growth and resilience in an increasingly complex business environment.
Information & Communication
Effective communication and information flow are indispensable for maintaining robust internal control within any organization. This critical component ensures that pertinent information is disseminated across all levels, equipping employees with the necessary knowledge to fulfill their responsibilities effectively.
By fostering transparency and accessibility, organizations empower their workforce to make informed decisions and contribute to the achievement of strategic objectives.
Moreover, this facet of internal control encompasses the establishment of channels through which feedback can be obtained. These channels serve as vital conduits for gathering insights from employees, stakeholders, and external sources.
By soliciting feedback, management gains valuable perspectives on emerging risks, operational inefficiencies, and opportunities for improvement. This real-time information enables management to stay abreast of evolving dynamics and adapt their strategies accordingly, thereby enhancing organizational agility and resilience.
In essence, effective communication and information flow serve as the lifeblood of internal control, facilitating collaboration, alignment, and informed decision-making across the organization.
By prioritizing transparency, accessibility, and feedback mechanisms, companies can strengthen their internal control processes and navigate the complexities of the business landscape with confidence and agility.
Monitoring Activities
Continuous monitoring is the final pillar of the COSO Framework, ensuring that internal control processes remain effective over time. This involves the ongoing assessment of control activities and the timely detection and remediation of deficiencies.
By establishing a systematic monitoring mechanism, companies can instill confidence in stakeholders and demonstrate their commitment to upholding robust internal controls.
Harnessing the Power of COSO Framework Components
Individually, each component of the COSO Framework plays a crucial role in enhancing organizational resilience. However, the synergy between these components truly unleashes their power. By aligning the control environment with risk assessment, companies can foster a culture of risk awareness and accountability.
Likewise, integrating control activities with information and communication channels ensures that internal control processes remain agile and responsive to emerging threats.
Conclusion
In an era of uncertainty and volatility, resilience emerges as a critical differentiator for businesses seeking to thrive amidst adversity.
The COSO Framework offers a structured approach to bolstering organizational resilience, encompassing five key components: control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring activities.
By harnessing the power of these components in concert, companies can confidently navigate complexities, ensuring sustainable growth and long-term success.