WiFi technology is an integral part of our daily lives, whether at home, in the workplace, or on mobile devices.
Despite the advancements in broadband technology, from the slow speeds of ADSL to the lightning-fast capabilities of fiber broadband, WiFi optimization remains crucial for achieving the best possible speeds and performance.
What Causes Slow Wifi Speeds?
Several factors can lead to frustratingly slow WiFi speeds:
- Interference: A common culprit for slow WiFi is interference, especially in the 2.4 GHz frequency band. This interference can stem from various sources, including neighboring WiFi networks.
- Legacy Equipment: The performance of your WiFi network is not only dependent on your router but also on the devices connecting to it. Older devices with outdated components can significantly slow down your network.
- Limited Range: WiFi signals are generally low in power, which limits their range. The further you are from the router, the weaker the signal, leading to reduced performance and speed. Physical obstructions like walls and floors can exacerbate this issue.
The Different Bands
WiFi operates on two main frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Understanding the differences between these bands is key to optimizing your WiFi network:
- 2.4 GHz Band: This band is more susceptible to interference but offers a wider coverage area. It’s compatible with most devices but can get congested, leading to slower speeds.
- 5 GHz Band: This band provides faster speeds and is less prone to interference. However, it has a shorter range and may not penetrate walls and floors as effectively as the 2.4 GHz band.
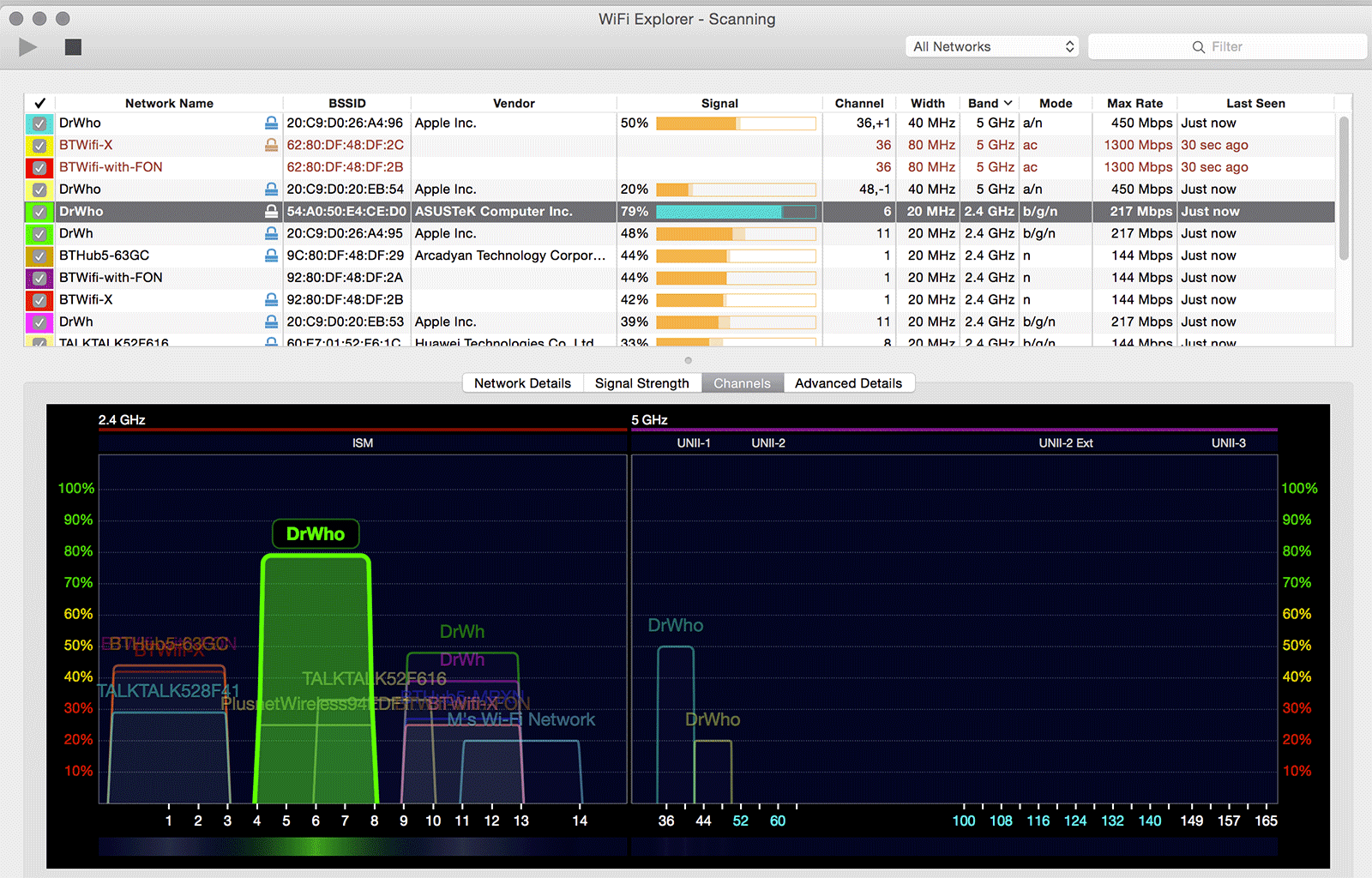
Wifi Spectrum Optimisation
Optimizing the WiFi spectrum is essential for deploying sufficient network capacity. A common approach is to add more access points.
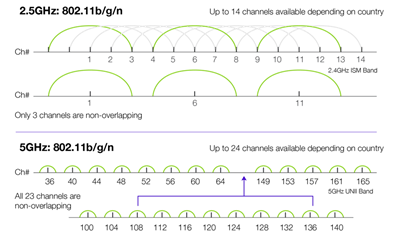
However, this can lead to spectrum limitations, particularly in the 2.4 GHz band, which only supports three non-overlapping channels. In contrast, the 5 GHz band can support up to 24 channels, depending on the location, offering a broader spectrum for network deployment.
Additional Strategies for WiFi Optimization
Channel Selection and Management
Proper channel selection, particularly in the 2.4 GHz band, can reduce interference. Tools and apps are available to analyze WiFi channels in your area and select the least congested one.
For example, Piso wifi users can handle issues like piso wifi 10.0.0.1 pause time with the help of the apps which can greatly optimise their Wifi service.
Update Firmware and Hardware
Regularly updating your router’s firmware can improve performance and security. Additionally, upgrading older routers or devices can significantly enhance your WiFi speed and reliability.
Optimize Router Placement
The placement of your router can greatly affect your WiFi’s performance. It should be centrally located, away from obstructions and interference sources like microwaves and cordless phones.
Use WiFi Extenders or Mesh Networks
For larger spaces, WiFi extenders or mesh network systems can help eliminate dead zones and provide consistent coverage throughout the area.
Prioritize Traffic with Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS settings in your router can prioritize bandwidth for critical tasks or devices, ensuring optimal performance for high-priority activities like video conferencing or streaming.
Conclusion
WiFi optimization is a multifaceted approach that involves understanding the limitations and capabilities of different frequency bands, managing your network’s spectrum, and making strategic choices about equipment and settings.
By addressing factors like interference, equipment quality, and network configuration, you can significantly enhance your WiFi experience.